"The Heart of the Matter: A Deep Dive into Cardiovascular Health"
World Heart Day 2023, observed on September 29th, stands as a global platform dedicated to raising awareness of cardiovascular health. This annual occasion serves to remind people worldwide of the paramount importance of heart health and aims to inspire individuals to proactively take steps to prevent heart disease. It’s noteworthy to emphasize that World Heart Day strongly advocates the adoption of healthier lifestyles, promoting regular physical activity, maintaining a balanced diet, quitting smoking, and managing stress.
Furthermore, this day underscores the critical significance of early detection and the prompt treatment of risk factors such as high blood pressure, elevated cholesterol levels, and diabetes. It encourages the populace to undergo regular health check-ups and endeavors to educate communities about the tell-tale signs and symptoms of heart disease.
World Heart Day also issues a collective call to action, summoning governments, healthcare organizations, and individuals to unite in the pursuit of policies and initiatives that foster heart-healthy environments and ensure equitable access to healthcare services.
Ultimately, World Heart Day serves as a poignant reminder that the responsibility of caring for our hearts extends beyond the individual—it is a collective endeavour with the noble intention of safeguarding the lives of millions across the globe.

The burden of cardiovascular disease (CVD) in India significantly exceeds global averages, with, for instance, an age-standardized death rate of 282 deaths per 100,000 in India compared to the global average of 233 deaths per 100,000. Recent trends have seen an increasing focus on tailoring treatment plans to an individual’s genetic makeup.
Furthermore, minimally invasive procedures, such as transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), have gained prominence. These procedures reduce recovery times and minimize complications. Additionally, advanced imaging technologies like 3D echocardiography and cardiac MRI have revolutionized the diagnosis and treatment planning process, enabling more precise interventions.
Artificial Intelligence plays a pivotal role by analyzing extensive datasets, contributing to risk prediction for heart disease, and aiding in surgical decision-making. It significantly enhances diagnostics and prognostics. Additionally, the exploration of stem cell therapies and gene therapies offers hope for repairing damaged heart tissue and addressing genetic heart conditions.
These remarkable advancements hold the promise of a brighter future for individuals with heart disease, offering treatments that are not only more effective but also tailored to individual needs, thus contributing to the global mission of reducing the burden of heart-related morbidity and mortality.
Cardiac catheterization and Coronary stenting
Cardiac catheterization, also known as coronary angiography, is a medical procedure employed for both diagnosing and treating heart-related conditions. This surgical technique involves the insertion of a slender, flexible tube called a catheter into a blood vessel, typically in the wrist. The catheter is then guided through the arteries until it reaches the heart.
To ensure the patient’s comfort and relaxation, necessary preparations are made, which may include the administration of local anesthesia and mild sedation. Under the guidance of X-ray imaging, a specialized catheter is carefully threaded through the blood vessel and directed toward the coronary arteries. A contrast dye is introduced through the catheter into the coronary arteries, which enhances their visibility on X-ray images. This allows the medical team to evaluate blood flow and detect any blockages or irregularities within the arteries.
Cardiac catheterization is a valuable diagnostic tool used to identify various conditions, including coronary artery disease, valve issues, and congenital heart disorders. It provides essential information about both the structure and function of the heart.
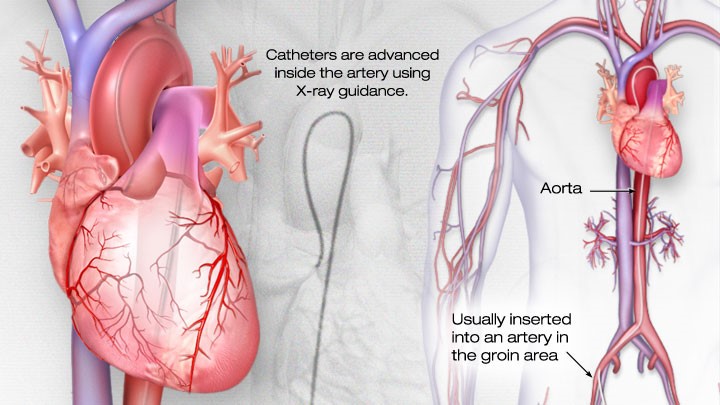
Conversely, coronary stenting is a medical procedure employed to address coronary artery disease, a condition characterized by the narrowing or blockage of blood vessels that supply the heart muscles due to the accumulation of fatty plaques. During this procedure, a small and expandable mesh device, commonly referred to as a stent, is carefully inserted into the affected section of the coronary artery.
The process typically begins with a coronary angiogram to visualize the narrowed or blocked artery. Once the blockage is precisely identified, a thin and flexible catheter featuring a deflated balloon at its tip is guided to the narrowed region. The balloon is then inflated, exerting pressure on the plaque within the artery, which effectively widens the vessel. After achieving the desired artery width, the stent, already mounted on the balloon, is expanded and left in place. The stent serves as a supportive scaffold, effectively maintaining the artery’s openness and facilitating improved blood flow to the heart muscle.
Subsequently, the balloon is deflated and removed, leaving the stent securely in position. Over time, the artery naturally heals around the stent, anchoring it firmly in place. Coronary stenting is effective in alleviating chest pain (angina) and enhancing blood flow to the heart, ultimately reducing the risk of heart attacks and mitigating complications associated with coronary artery disease. Importantly, this procedure is often minimally invasive, resulting in shorter recovery times compared to traditional open-heart surgery.
High blood pressure hypertension treatments
Treatment for high blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is crucial as it’s a common medical condition characterized by consistently high force of blood against artery walls. If left unmanaged, it can lead to serious health issues such as heart disease, stroke, and kidney damage. Various treatment options are available:
- Lifestyle Modifications: Often, the initial approach involves making lifestyle changes. These include adopting a heart-healthy diet like the DASH diet, reducing salt intake, increasing physical activity, limiting alcohol consumption, quitting smoking, and effectively managing stress.
- Medications: When lifestyle changes aren’t enough, healthcare providers may prescribe medications. Commonly used antihypertensive drugs include diuretics, beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers, and calcium channel blockers.
- Complementary Therapies: Complementary therapies like acupuncture, meditation, or biofeedback can be beneficial in managing stress and reducing blood pressure.
- Regular Monitoring: Regular blood pressure checks are essential to track progress and make necessary adjustments to the treatment plan. Maintaining a healthy weight can also significantly contribute to reducing blood pressure. If hypertension is a secondary condition resulting from an underlying medical issue (such as kidney disease or hormonal disorders), addressing that underlying condition is vital in controlling blood pressure.
Heart Attack Treatment:
Treatment for a heart attack, medically termed as a myocardial infarction (MI), is an urgent medical response aimed at restoring blood flow to the heart muscle while preventing further damage. The treatment begins with immediate medical attention, where medications are administered to relieve symptoms, reduce pain, and stabilize the heart. These medications often include aspirin, nitroglycerin, and antiplatelet agents.
Restoring blood flow to the blocked coronary artery is a top priority. This can be achieved through thrombolytic drugs or percutaneous coronary intervention procedures such as angioplasty and stent placement. Following a heart attack, a structured cardiac rehabilitation program is usually recommended to aid in recovery. This program encompasses exercises, education on heart-healthy lifestyle changes, and emotional support.
Patients who have experienced a heart attack are typically prescribed medications like beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, statins, and antiplatelet drugs to reduce the risk of future cardiac events. Embracing a heart-healthy lifestyle, which includes dietary improvements, regular exercise, quitting smoking, and effective stress management, is vital for long-term recovery and prevention of future heart attacks.
The primary goal is to minimize heart muscle damage, restore cardiac function, and reduce the risk of recurrent heart events, ultimately enhancing the patient’s quality of life and prognosis.
Atrial Arrhythmia Treatment:
Atrial arrhythmias, which are irregular heart rhythms originating in the heart’s upper chambers (atria), necessitate tailored treatment based on their specific type, severity, and underlying causes. Common approaches include:
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs: These medications are often prescribed to regulate the heart’s rhythm and rate in atrial arrhythmias. They work by controlling the electrical impulses within the heart.
- Electrical Cardioversion: This procedure involves delivering a controlled electrical shock to the heart to restore a normal rhythm. It is typically used for acute episodes of atrial fibrillation (AF) or atrial flutter.
- Catheter Ablation: This surgical procedure targets and eliminates the abnormal tissue responsible for the arrhythmia. It is effective for certain types of atrial arrhythmias, especially when medications are ineffective or not well-tolerated.
- Atrial arrhythmias, especially atrial fibrillation (AF), can increase the risk of blood clots and stroke. Consequently, anticoagulant medications may be prescribed to mitigate this risk.
- Lifestyle changes, such as reducing alcohol and caffeine intake, managing stress, and maintaining a healthy weight, can be beneficial in managing atrial arrhythmias. The specific therapy chosen depends on factors like the nature of the arrhythmia, its duration, the patient’s overall health, and individual risk factors.
Angina Treatment:
Angina, a manifestation of coronary artery disease, presents as chest pain or discomfort due to reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. Treatment primarily involves:
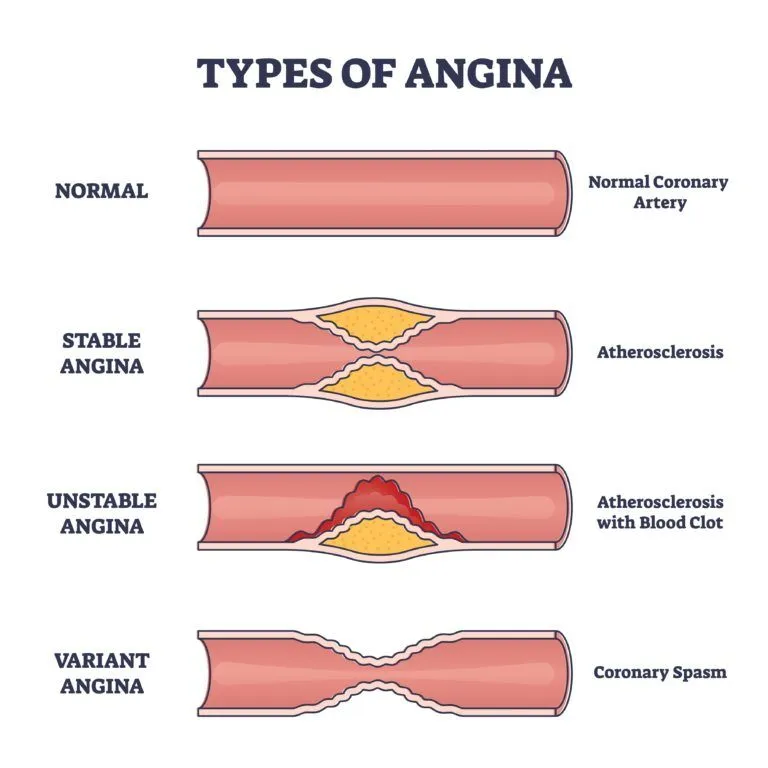
- The use of medications like Nitro-glycerine and other drugs to alleviate angina symptoms by relaxing and dilating blood vessels.
- Medications to manage risk factors, such as statins for cholesterol control and antihypertensive drugs for blood pressure management.
- Cardiac rehabilitation exercises are recommended as part of the treatment plan.
Cardiac Insufficiency Treatment:
Cardiac insufficiency, or heart failure, is a chronic condition characterized by the heart’s inability to effectively pump blood, resulting in symptoms like fatigue, breathlessness, and fluid retention. Treatment goals include symptom improvement, enhanced quality of life, and slowing disease progression. Treatment strategies comprise:
- Medications like diuretics to reduce fluid build-up, ACE inhibitors or ARBs to relax blood vessels, beta-blockers to lower heart rate, and drugs like digoxin to strengthen heart contractions.
- Patients are advised to adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle, which includes managing weight, following a low-salt diet, limiting alcohol and caffeine intake, and quitting smoking.
- Regular exercise, in accordance with the doctor’s recommendations, can help improve heart function.
- Regular check-ups and monitoring of vital signs, fluid retention, and blood tests are crucial.
- In advanced cases, procedures like coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or heart transplant may be considered.
- Patients and their families should receive education on symptom management, recognizing worsening conditions, and adhering to the prescribed treatment plan. Overall, the treatment approach for cardiac insufficiency involves a combination of medications, lifestyle modifications, and medical oversight to enhance the patient’s well-being and slow the progression of the disease.
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD) Treatments:
Coronary artery disease (CAD), characterized by the narrowing or blockage of coronary arteries supplying the heart muscle with oxygen and nutrients, necessitates comprehensive treatment strategies:
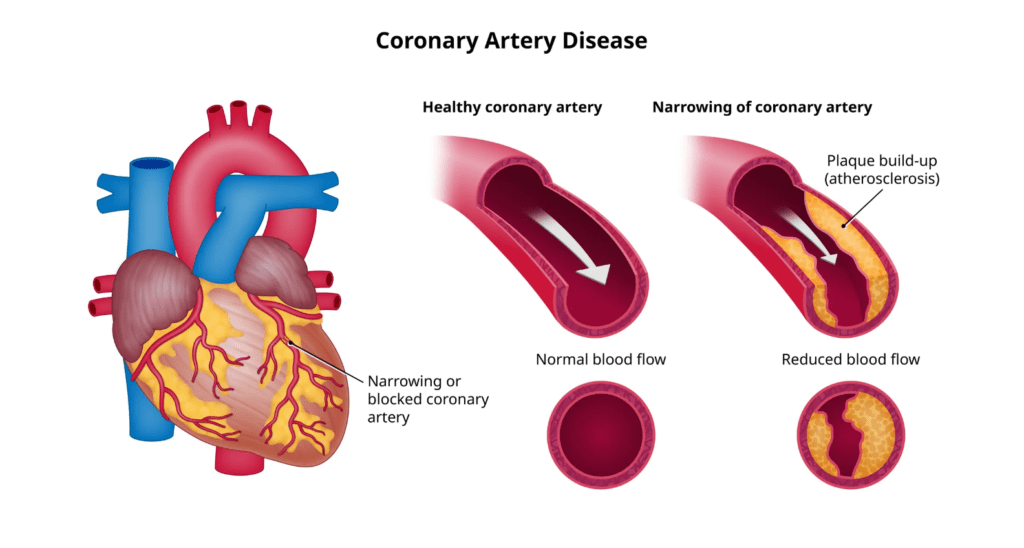
- Lifestyle modifications, medications, angioplasty, and stent placement are preferred approaches.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) involves bypassing blocked arteries using healthy blood vessels from elsewhere in the body to improve blood flow to the heart.
- Cardiac rehabilitation programs offer exercise training, dietary guidance, and emotional support to aid patients in their recovery.
- CAD treatment often combines these approaches, tailored to each patient’s specific condition and needs, aiming to manage symptoms and reduce the risk of heart attacks and other complications



