"Unlocking the Secrets to Thriving with Diabetes: Your Comprehensive Guide to Better Health!"
Diabetes-Tip 1 -Reducing Carbohydrates Intake
An effective approach to managing Diabetes involves carefully managing your carbohydrate intake. Carbohydrates can significantly impact blood sugar levels, so it’s crucial to make wise choices regarding the type of carbohydrates you consume and control your portion sizes. It’s beneficial to concentrate on incorporating resistant carbohydrates, which are present in foods like sweet potatoes, regular potatoes, yams, and various root vegetables. These foods not only provide essential nutrients but also have a slower digestion rate due to their high fiber content, resulting in a more gradual increase in blood sugar levels. Furthermore, it’s important to prioritize foods rich in dietary fiber, as they play a role in stabilizing blood sugar levels and promoting feelings of fullness. It’s advisable to be cautious of processed carbohydrates, including sugary snacks and refined grains like white bread, rice, wheat, and ragi, as they can lead to rapid spikes in blood sugar levels.
Let’s have this breakfast every day for those who have Diabetes
– 40-gram Nuts (40-50 groundnuts ,5-6 almonds , 3-4 cashews )
– 1-2 boiled eggs or any form of eggs
– 1 Dosa or idly or chapatti, which is less than 50gram (use ghee)
– 1 cup coconut chutney or Peanut chutney
– Coffee or tea (No sugar or milk)
– 50-100gram guava or banana as a fruit.

Diabetic Tips 2: Include more vegetables for better Diabetic management
Incorporating vegetables into your meals is a vital practice for individuals managing Diabetes. Extensive research consistently underscores the advantages of integrating vegetables into your diet, especially when it comes to Diabetes management. Strive to have vegetables cover half of your lunch and dinner plates to maximize their positive impact.
Vegetables are renowned for being low in calories and carbohydrates, making them an excellent choice for those managing Diabetes. Furthermore, they are rich in dietary fiber, a key component that plays a pivotal role in regulating blood sugar levels by slowing down the digestion and absorption of carbohydrates. Additionally, fiber contributes to a sense of fullness, which can be beneficial for weight management.

Scientific studies have underscored the numerous benefits of a diet rich in vegetables for individuals with Diabetes. For example, research published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition has demonstrated that increased vegetable consumption can reduce the risk of developing type 2 Diabetes. Similarly, a study conducted by the Harvard School of Public Health has shown that a higher intake of green leafy vegetables such as spinach and kale is associated with a reduced risk of type 2 Diabetes. These findings further emphasize the importance of incorporating vegetables into your daily meals. To ensure you obtain vital nutrients while effectively managing Diabetes, consider incorporating locally sourced fresh vegetables into your daily lunch and dinner. Aim to have 50% of your plate filled with these nutritious vegetables. Maintain this practice for a period of one to two months, and observe the impact it has on your blood glucose levels.
Diabetic Tips 3- The Power of Exercise
Insulin resistance is a prevalent issue in type 2 Diabetes, characterized by cells’ poor responsiveness to the hormone insulin. Exercise has emerged as a crucial strategy to combat insulin resistance and enhance cellular sensitivity to insulin. One simple yet effective exercise that can contribute to this effort is the act of sitting down and then standing up from a chair. This exercise engages major muscle groups in the body and can lead to a reduction in insulin resistance and blood sugar levels.
When you engage in physical activity, the contraction of your muscles triggers a signalling pathway known as AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). This pathway serves as a cellular energy sensor. AMPK, in turn, activates various targets that play a role in how your body processes glucose. One significant outcome of this activation is the facilitation of glucose transporter molecules, known as GLUT4, moving to the surface of your cells. This relocation makes it easier for your cells to take in glucose. Consequently, this process enhances your body’s ability to manage glucose effectively and helps maintain healthy blood sugar levels.

When you engage in physical activity, the contraction of your muscles triggers a signalling pathway known as AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK). This pathway serves as a cellular energy sensor. AMPK, in turn, activates various targets that play a role in how your body processes glucose. One significant outcome of this activation is the facilitation of glucose transporter molecules, known as GLUT4, moving to the surface of your cells. This relocation makes it easier for your cells to take in glucose. Consequently, this process enhances your body’s ability to manage glucose effectively and helps maintain healthy blood sugar levels.
The Sit-to-Stand exercise, though seemingly straightforward, engages a multitude of crucial muscles throughout your body. These muscles collectively constitute a significant portion, approximately 50-70%, of the body’s total muscle mass. They encompass various muscle groups, including the quadriceps femoris (thighs), gluteal muscles (buttocks), hamstrings (back of thighs), gastrocnemius and soleus (calves), abdominal muscles (stomach), erector spine (lower back), deltoids (shoulders), and pectorals (chest). The activation of these muscles during this exercise plays a pivotal role in enhancing your body’s responsiveness to insulin, a key factor in regulating blood sugar levels and managing Diabetes.
Continued research into the virus’s transmission and potential treatments are essential for preparedness and response to future outbreaks. By implementing public health measures and raising awareness about MERS, we can take steps towards safeguarding communities and preventing the further spread of this enigmatic respiratory illness.
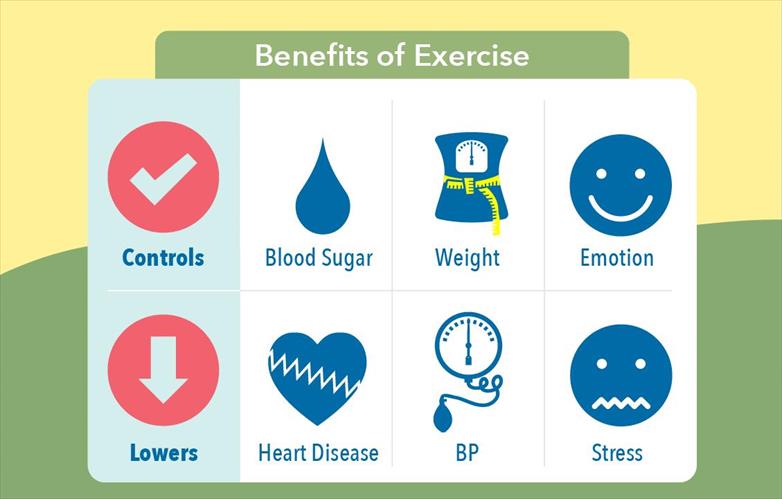
Consistently incorporating this exercise into your routine can lead to several benefits, including:
- Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Regularly performing the Sit-to-Stand exercise can enhance your body’s sensitivity to insulin, helping it manage blood sugar levels more effectively.
- Increased Caloric Expenditure: This exercise can contribute to burning calories, which can be beneficial for weight management, another essential aspect of Diabetes care.
- Enhanced Muscle Strength and Function: Over time, the Sit-to-Stand exercise can help strengthen and improve the functionality of the various muscle groups involved, promoting overall physical fitness.
Incorporating this exercise into your daily routine can be a valuable component of a comprehensive approach to Diabetes management.
As we age, it’s natural for our muscle mass to decline, which can contribute to elevated blood sugar levels. To counteract this effect, incorporating a straightforward exercise like the Sit-to-Stand Exercise into your daily routine can be highly beneficial. Aim for 20 repetitions of this exercise, repeated 3-5 times throughout the day, to maximize its advantages. The beauty of this exercise is its simplicity and convenience, as it can be performed at any time and in any place.



