*EARLY DIAGNOSIS OF DEMENTIA *
Dementia is a progressive and debilitating neurological condition characterized by a decline in cognitive capabilities, including memory, thinking, communication, problem-solving, and behaviour. This condition can also lead to mood changes. The most common causes of dementia include Alzheimer’s Disease, vascular dementia, and Lewy body dementia. Dementia typically impacts daily functioning and quality of life, often requiring caregiving and support. Although there is no cure for most types of dementia, early diagnosis and interventions can help manage symptoms and improve the well-being of individuals affected.
Dementia presents significant challenges for those diagnosed with the condition and their families. It underscores the importance of awareness, research, and support for affected individuals and caregivers. Over the years, the terminology and understanding of dementia have evolved. Previously, the term “senile dementia” was used to describe dementia in older people, but this term is now considered offensive and outdated. Today, doctors use more specific terms, such as Alzheimer’s Disease or other types of dementia, to describe age-related cognitive decline. It’s important to note that dementia is not an inevitable part of aging, but it does become more common with increasing age.
Vascular dementia is another prevalent form of dementia, often caused by insufficient blood flow to the brain, typically due to conditions like high blood pressure, diabetes, smoking, or heart disease. The symptoms of vascular dementia may vary depending on the underlying causes and the extent of brain damage. They can include problems with thinking, memory, and other mental abilities.
Frontotemporal dementia, or frontal lobe dementia, is a relatively rare type of dementia that primarily affects the frontal and temporal lobes of the brain. Unlike Alzheimer’s Disease, FTD often occurs at a younger age, typically between 40 and 65 years old. FTD is characterized by the accumulation of abnormal proteins in the brain and leads to progressive cognitive and functional decline. Diagnosis and care should involve specialists familiar with the complexities of FTD, as it requires tailored interventions and support for both individuals with FTD and their families.
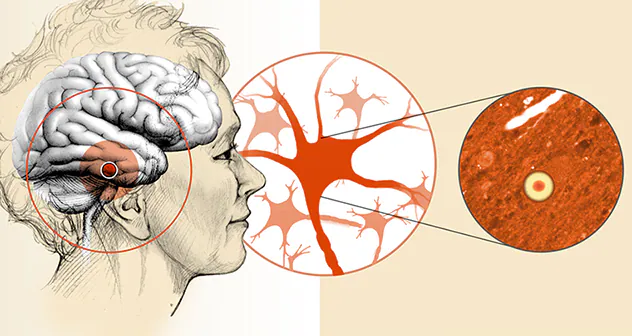
It’s important to understand that dementia comprises various types, each with distinct characteristics and underlying causes. Alzheimer’s disease is the most prevalent form, marked by progressive memory loss, confusion, and difficulties with problem-solving and language. Abnormal protein deposits in the brain are a hallmark of Alzheimer’s.

Lewy body dementia is a complex and progressive neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the accumulation of abnormal protein deposits called Lewy bodies in the brain. LBD shares similarities with both Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases and leads to a range of cognitive, motor, and psychiatric symptoms.
Early diagnosis of dementia is crucial fol for several reasons, including effective intervention. Medications and r several reasons, including effective intervention. Medications and lifestyle changes can manage symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals with dementia. Early diagnosis also allows individuals and their families time to make important decisions about legal, financial, and healthcare matters, such as setting up advance directives, making caregiving arrangements, and managing finances to meet future needs. Recognizing the early signs of dementia in women is essential for timely intervention and support. These signs may include memory loss, difficulty with familiar tasks, disorientation, mood changes, and more.
Additionally, there is ongoing research into potential treatments and interventions for dementia. Curcumin, a compound found in turmeric, has shown promise in providing neuroprotection, combating oxidative stress and neuroinflammation, and enhancing memory and cognitive function in the context of dementia.
Conclusion
Dementia is a complex and challenging condition that affects individuals and their families. It is essential to raise awareness, promote research, and provide support for those dealing with dementia to improve the quality of life for affected individuals and their caregivers. Early diagnosis, appropriate care, and ongoing research are essential in the fight against this condition.



