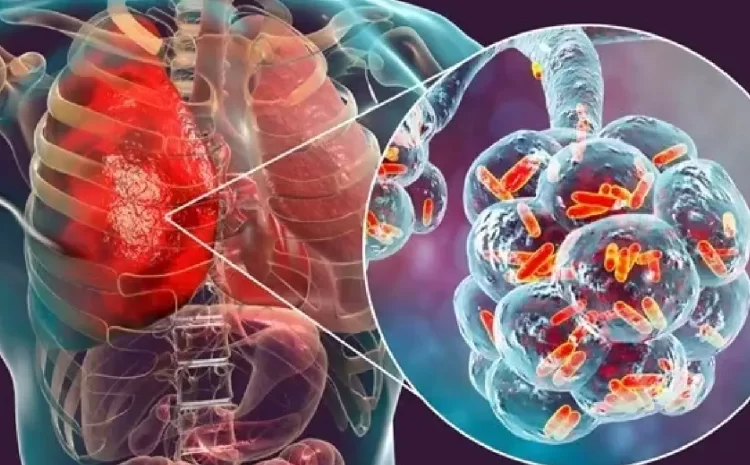
Pneumonia is an infection that inflames the air sacs in the lungs, filling them with fluid or pus and making breathing difficult. It can be triggered by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or inhaling irritants. Common signs include cough, fever, shortness of breath, and chest pain. While mild cases can be treated at home, severe infections may require hospitalization.
Causes and Types of Pneumonia
The severity of pneumonia varies based on its cause and the patient’s overall health.
- Bacterial Pneumonia – The most frequent type, often caused by Streptococcus pneumoniae. Symptoms appear suddenly, including high fever, chills, chest pain, and a phlegmy cough. Antibiotics are usually effective.
- Viral Pneumonia – Triggered by viruses like influenza or COVID-19, symptoms are typically milder than bacterial cases. However, severe viral pneumonia can lead to complications, and antibiotics don’t work against viruses.
- Fungal & Aspiration Pneumonia – Less common but serious. Fungal pneumonia affects those with weakened immune systems, often due to spore inhalation. Aspiration pneumonia occurs when food, liquids, or vomit enter the lungs, causing infection.
- Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia – Develops in hospitalized patients and tends to be more drug-resistant. Community-Acquired Pneumonia is contracted in everyday settings and is generally easier to treat.
Symptoms of Pneumonia
Symptoms vary by age, health status, and the infection’s cause. Early detection and treatment are crucial to preventing complications.
How Pneumonia Spreads: Is It Contagious?
Most types of pneumonia are contagious, though some develop from existing conditions or environmental factors.
- Respiratory Droplets – Viral and bacterial pneumonia often spread through coughs or sneezes. Close contact in crowded areas increases risk.
- Surface Transmission – Germs can survive on hands and objects. Touching contaminated surfaces and then your face can lead to infection. Proper handwashing reduces this risk.
The Global Impact of Pneumonia
Pneumonia remains a leading cause of death worldwide, especially among children, the elderly, and immunocompromised individuals. According to the WHO, it’s a major public health issue, particularly in low-resource areas with limited healthcare access.
In 2024, pneumonia claimed over 127,000 young lives in India, contributing to 700,000 global child deaths—making it the deadliest infectious disease for children under five. World Pneumonia Day (November 12, 2024) highlighted this crisis with the theme: “Every Breath Counts: Stop Pneumonia in Its Tracks.”
Recognizing Severe Symptoms
Early signs include persistent cough, fatigue, fever, and breathlessness. Severe cases may involve:
- Difficulty breathing
- High fever or chest pain
- Bluish lips/nails (oxygen deprivation)
- Confusion (especially in seniors)
Children may show rapid breathing or lethargy, while older adults might experience confusion without typical respiratory symptoms.
Preventing Pneumonia
Protection involves vaccines, hygiene, and healthy habits:
Vaccination – Pneumococcal and flu shots are highly effective.
Hygiene – Regular handwashing, avoiding sick individuals, and wearing masks in high-risk areas help.
Lifestyle – A balanced diet, exercise, and quitting smoking strengthen immunity.
High-risk groups (infants, elderly, immunocompromised) should take extra precautions.
Diagnosis & Treatment
Doctors use stethoscopes, chest X-rays, blood tests, and sputum analysis to diagnose pneumonia. Treatment depends on the cause:
- Bacterial – Antibiotics
- Viral – Antivirals (if severe) + rest
- Severe Cases – Hospitalization, oxygen therapy, IV fluids
High-Risk Groups & Complications
- Children – Rapid breathing, feeding difficulties; need prompt care.
- Elderly – May show confusion instead of fever; high risk of severe progression.
Complications can include:
- Lung abscesses (pus-filled cavities)
- Pleural effusion (fluid around lungs)
- Respiratory failure or sepsis (life-threatening)
Recovery & Long-Term Care
Recovery time varies—mild cases improve in weeks, severe cases may take months. Key steps include:
- Nutrition – Protein, vitamins, and hydration aid healing.
- Rest & Gradual Activity – Avoid overexertion; prioritize sleep.
- Avoid Irritants – No smoking; limit exposure to pollution.
Conclusion
Pneumonia remains a major health threat, but vaccination, early treatment, and prevention can save lives. Awareness and proactive measures are essential for protecting vulnerable populations and maintaining lung health.



