Though clinically termed as Haemorrhoids, the colloquial familiarity with the masses for the same is as Piles/it is commonly known among the masses as Piles.
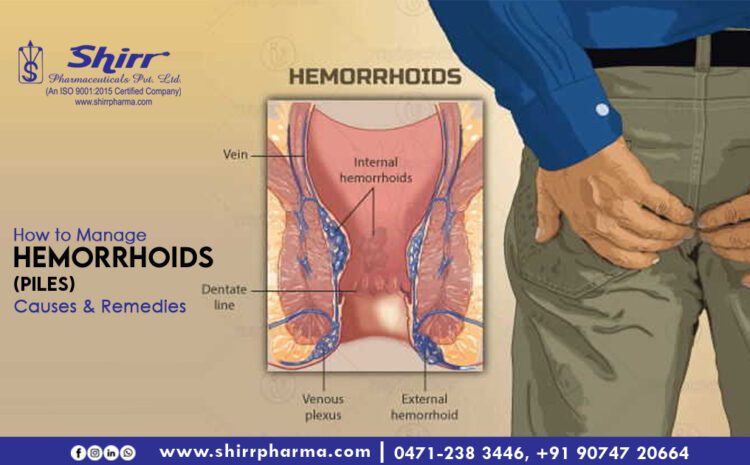
A medical condition caused by swollen veins in the lower rectum or anus that becomes painful, based on the location of the lump, haemorrhoids can be classified as Internal or External.
- Internal haemorrhoids evolve and appear within the rectum and are comparatively less aggravating and agonizing because this area has few pain receptors, however, the same can also cause bleeding when infuriated.
- External haemorrhoids develop and appear at the opening of the anus, cause swelling and are tormenting.
- In certain cases, both the internal and external haemorrhoids emerge together, simultaneously.
Haemorrhoids are generally characterized by itching and irritation accompanied by aches and pain, sometimes bleeding while defecating.
CAUSES
Common signs and symptoms include :
Haemorrhoids are caused by increased pressure or due to excessive strain in the lower rectum, during the bowel movement, causing the blood vessels around the anus and
Rectum to stretch and swell, forming piles. This may be mainly attributed and not limiting to
- Constipation
- Straining while defecating
- Pregnancy
- Certain comorbidities
- Age and biological inheritance
- Protracted sitting hours
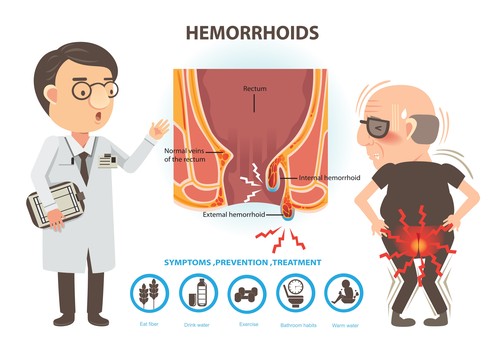
PREVENTION ADVICE
Haemorrhoids in most cases are self-healing. However, certain home remedies and lifestyle can significantly help reduce the discomfort that people experience
- Increase in intake of Fibre rich diet consisting of whole/bran grains, vegetables and fruits.
- Increase in water consumption, at least 8 to 10 glasses of water per day.
- Engaging in regular exercise and physical activities.

TREATMENT METHODOLOGY
- Soaking the anal area with salt infused warm sitz baths.
- Prescription based laxatives and corticosteroids.
- Surgical options are considered where in non-invasive therapies fail to yield the desired result. The following procedures may be initiated by the doctor, post assessment of the haemorrhoid grade status ranging from 1 to 4.
- Banding: An elastic band is placed around the base of the haemorrhoid, cutting off its blood supply, resulting in its fall. This is effective for treating all haemorrhoid of less than grade 4 status.
- Sclerotherapy: A medication is injected to make the haemorrhoid shrink and shrivel. This is effective for grade 2 and 3 haemorrhoid and is an alternative to banding.
- Infrared coagulation: A device is used to burn the haemorrhoid. This technique is used to treat grade I and II haemorrhoids.
- Haemorrhoidectomy: Here, the excess tissue that causes bleeding is surgically removed. This can be done in various ways and may involve a combination of a local or a general anaesthetic. It is the most effective surgical procedure for complete removal of haemorrhoids. Although there is a risk of certain complications, including difficulties with passing stools, as well as urinary tract infections



